4. Financial Functions
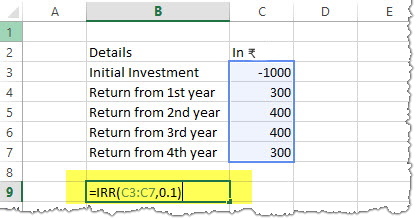
4.1 IRR Financial Function
Returns the internal rate of return for a series of cash flows represented by the numbers in values. These cash flows do not have to be even, as they would be for an annuity. However, the cash flows must occur at regular intervals, such as monthly or annually. The internal rate of return is the interest rate received for an investment consisting of payments (negative values) and income (positive values) that occur at regular periods.
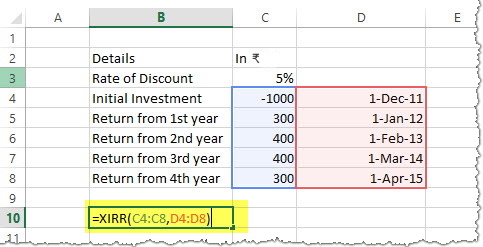
4.2 XIRR: Financial Function
Returns the internal rate of return for a schedule of cash flows that is not necessarily periodic. To calculate the internal rate of return for a series of periodic cash flows, use the IRR function.

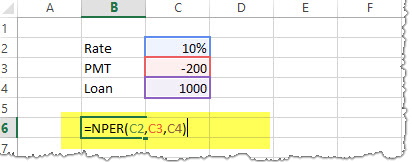
4.3 NPER: Financial Function
Returns the number of periods for an investment based on periodic, constant payments and a constant interest rate.
Example₹200 is paid per year for a loan of ₹1000. The interest rate is 10% p.a. and the payment needs to be done yearly. Find out the NPER.
Solution: We need to calculate NPER in the following manner
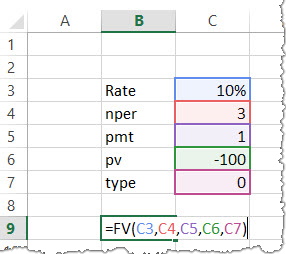
4.4 Future Value (FV): Financial Function
FV, calculates the future value of an investment based on a constant interest rate. You can use FV with either periodic, constant payments, or a single lump sum payment.
ExampleA has invested the ₹100 in 2018. The payment has been made yearly. The interest rate is 10% p.a. What would be the FV in 2021?
Solution: In excel, we will put the equation as follows
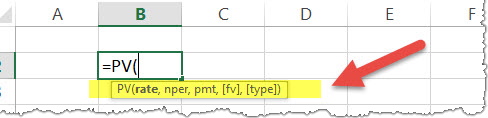
4.5 Present Value (PV): Financial Function
PV, one of the financial functions, calculates the present value of a loan or an investment, based on a constant interest rate. You can use PV with either periodic, constant payments (such as a mortgage or other loan), or a future value that's your investment goal.
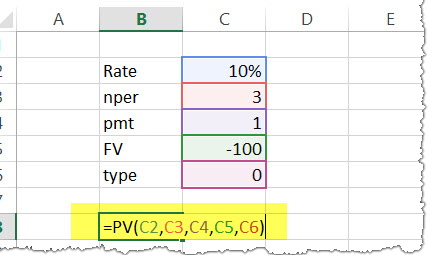
Example:
The future value of an investment in the ₹100 in 2019. The payment has been made yearly. The interest rate is 10% p.a. What would be the PV as of now?
Solution: In excel, we will put the equation as follows
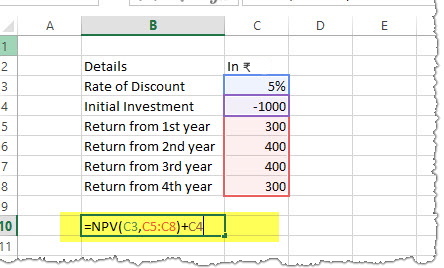
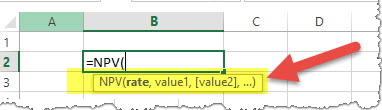
4.6 Net Present Value (NPV): Financial Function
Calculates the net present value of an investment by using a discount rate and a series of future payments (negative values) and income (positive values).
Example:
Here is a series of data from which we need to find NPV.
| Details | In ₹ |
|---|---|
| Rate of Discount | 5% |
| Initial Investment | -1000 |
| Return from 1st year | 300 |
| Return from 2nd year | 400 |
| Return from 3rd year | 400 |
| Return from 4th year | 300 |
Solution: In excel, we will put the equation as follows